Introduction
Ransomware has become one of the most dangerous cyber threats in the digital age, crippling businesses, governments, and individuals worldwide. From hospitals to Fortune 500 companies, no organization is immune.
This comprehensive guide covers:
- What ransomware is and how it works
- Different types of ransomware
- Notable ransomware attacks
- How ransomware spreads
- Prevention and mitigation strategies
- Best tools for ransomware protection
- What to do if you’re infected
By the end, you’ll understand how ransomware operates and how to defend against it effectively.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is malicious software (malware) that encrypts files or locks systems, demanding payment (usually in cryptocurrency) to restore access. Cybercriminals use it to extort money from victims, often threatening to leak data if the ransom isn’t paid.
How Ransomware Works
- Infection – Delivered via phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploits.
- Execution – Encrypts files, making them inaccessible.
- Ransom Demand – Displays a payment demand (often in Bitcoin or Monero).
- Decryption (or Not) – If paid, attackers may provide a decryption key (but often don’t).
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, ransomware damages will exceed $265 billion annually by 2031, with attacks occurring every 2 seconds.
Types of Ransomware
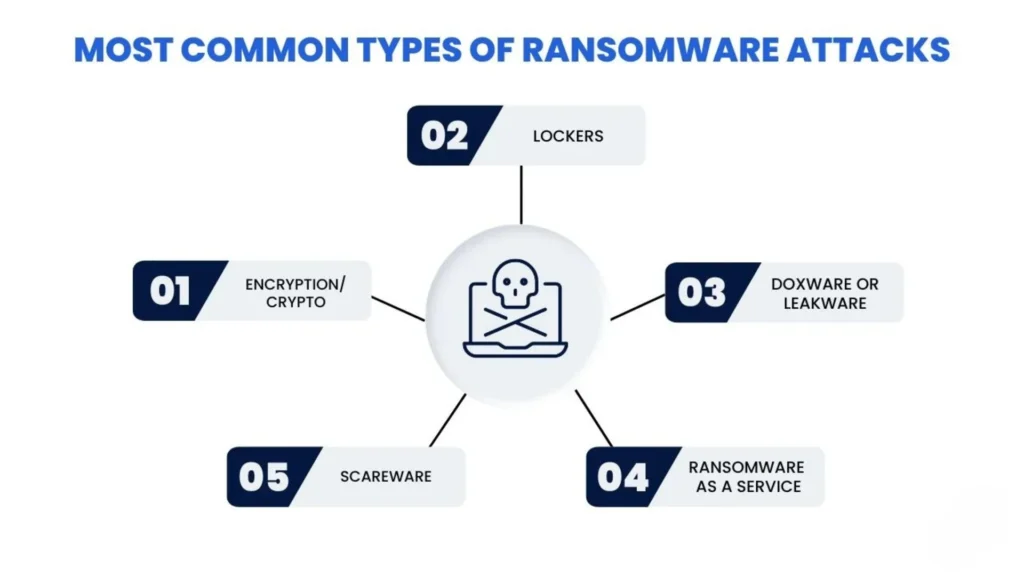
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Encrypting Ransomware | Encrypts files and demands payment for decryption | WannaCry, Locky |
| Locker Ransomware | Locks the entire system, preventing access | WinLocker |
| Scareware | Fake alerts claiming malware infection | FBI MoneyPak Scam |
| Doxware (Leakware) | Threatens to publish stolen data | REvil, Maze |
| RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) | Criminals rent ransomware tools to others | DarkSide, Conti |
How Ransomware Spreads
Ransomware infiltrates systems through:
1. Phishing Emails
- Fake invoices, job offers, or urgent messages with malicious attachments.
- Example: 2020 Garmin Attack
2. Malicious Websites & Drive-by Downloads
- Compromised sites that silently install ransomware.
3. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Attacks
- Weak passwords allow brute-force attacks.
4. Software Vulnerabilities
- Exploiting unpatched systems (e.g., WannaCry used EternalBlue).
5. USB & Removable Media
- Infected USB sticks spread ransomware offline.
Notable Ransomware Attacks
| Attack | Year | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| WannaCry | 2017 | Affected 200,000+ systems in 150 countries |
| NotPetya | 2017 | Caused $10B in damages, disguised as ransomware but was wiper malware |
| Colonial Pipeline | 2021 | Led to fuel shortages in the U.S., $4.4M ransom paid |
| Kaseya VSA | 2021 | Hit 1,500+ businesses via supply chain attack |
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
1. Employee Training
- Teach staff to recognize phishing emails (CISA Phishing Guide).
2. Regular Backups (3-2-1 Rule)
- 3 copies, on 2 different media, with 1 offline backup.
3. Patch Management
- Keep OS and software updated to block exploit-based attacks.
4. Use Endpoint Protection
- Deploy next-gen antivirus (e.g., CrowdStrike, SentinelOne).
5. Disable Macros & Limit RDP Access
- Restrict remote access and enforce MFA.
6. Network Segmentation
- Isolate critical systems to prevent lateral movement.
7. Email Filtering
- Use AI-based filters (e.g., Proofpoint, MimeSecure) to block malicious emails.
What to Do If Infected?
- Isolate the Infection – Disconnect from networks.
- Do NOT Pay the Ransom – No guarantee of recovery; funds criminal activity.
- Report to Authorities – Contact FBI’s IC3 (Internet Crime Complaint Center).
- Restore from Backups – Use clean, offline backups.
- Engage Cybersecurity Experts – Forensic analysis to prevent recurrence.
Best Ransomware Protection Tools
| Tool | Type | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Bitdefender GravityZone | Endpoint Protection | AI-based ransomware detection |
| Acronis Cyber Protect | Backup & Security | Automated recovery & anti-ransomware |
| CrowdStrike Falcon | EDR | Real-time threat hunting |
| Malwarebytes Anti-Ransomware | Anti-Malware | Blocks ransomware behavior |
Conclusion: Stay Ahead of Ransomware
Ransomware is evolving, but with proactive defense strategies, businesses can minimize risks. Key takeaways:
✅ Train employees to spot phishing.
✅ Maintain backups (test them regularly).
✅ Use advanced security tools (EDR, email filtering).
✅ Never pay the ransom – it fuels more attacks.
For more cybersecurity insights, check:
Has your organization faced a ransomware attack? Share your experience in the comments!

