Introduction
As businesses increasingly migrate to cloud computing, ensuring robust cloud security has become a top priority. The cloud offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, but it also introduces new security challenges. Cyber threats such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and malware attacks are on the rise, making cloud security essential for organizations of all sizes.
This article explores what cloud security is, why it matters, key challenges, and the best tools and applications to secure your cloud environment.
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security refers to a set of policies, technologies, and controls designed to protect cloud-based systems, data, and infrastructure from cyber threats. It ensures:
- Data confidentiality – Preventing unauthorized access.
- Data integrity – Ensuring data is not altered or corrupted.
- Data availability – Guaranteeing data is accessible when needed.

Cloud security applies to public, private, and hybrid cloud environments and involves multiple layers of protection.
Why is Cloud Security Important?
- Protection Against Data Breaches
- High-profile breaches (e.g., Capital One, SolarWinds) highlight the risks of poor cloud security.
- Stolen data can lead to financial losses and reputational damage.
- Compliance with Regulations
- Laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA require strict data protection measures.
- Non-compliance can result in hefty fines.
- Preventing Insider Threats
- Employees or contractors with malicious intent can exploit weak security.
- Securing Multi-Cloud Environments
- Many businesses use multiple cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), increasing complexity.
Key Cloud Security Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Misconfigured Cloud Settings | Default settings may leave data exposed. |
| Insecure APIs | Poorly secured APIs can be exploited by hackers. |
| Lack of Visibility | Difficulty monitoring data across cloud services. |
| Data Loss | Accidental deletion or ransomware attacks. |
| Account Hijacking | Stolen credentials leading to unauthorized access. |
Cloud Security Best Practices
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
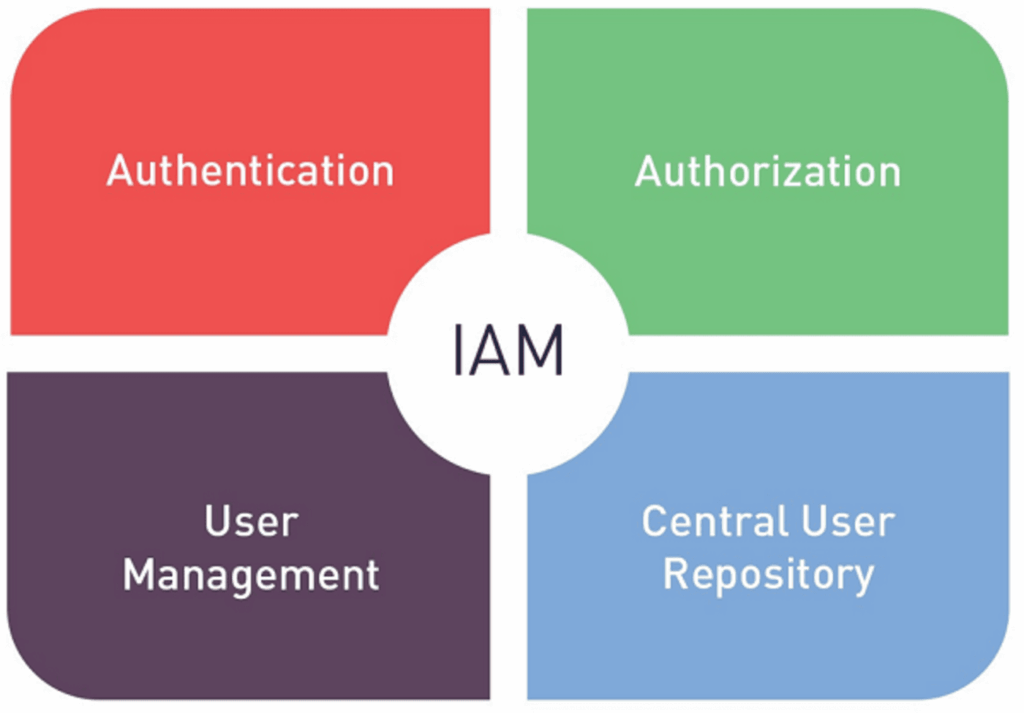
- Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) – Grant users only the access they need.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adds an extra layer of security.
- Example Tools:
- AWS IAM (Amazon Web Services Identity and Access Management)
- Azure Active Directory (Microsoft’s cloud IAM solution)
2. Encryption
- Data-at-rest encryption (e.g., AWS S3 Encryption, Azure Storage Service Encryption)
- Data-in-transit encryption (TLS/SSL protocols)
- Example Tools:
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
- Google Cloud Key Management
3. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
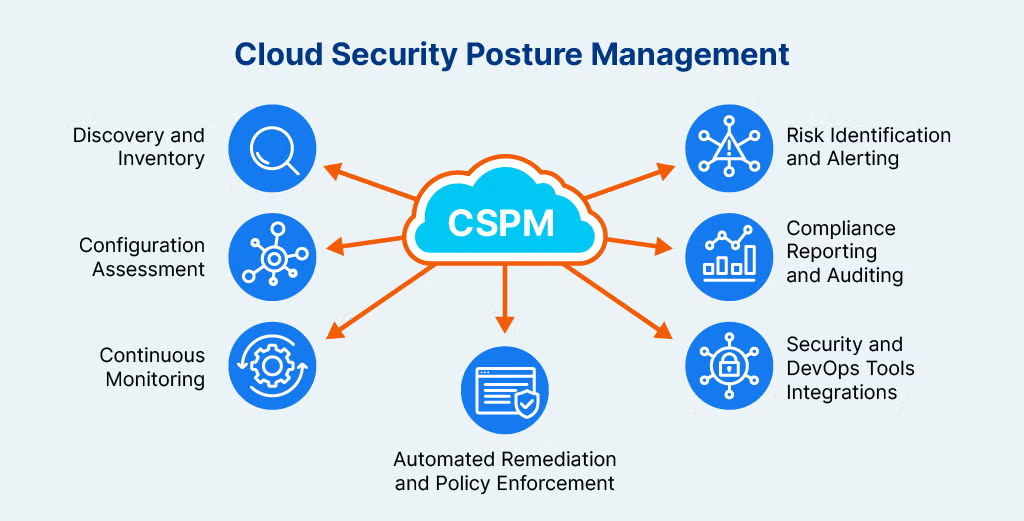
- Automatically detects and fixes misconfigurations.
- Example Tools:
- Prisma Cloud (by Palo Alto Networks)
- AWS Security Hub
4. Intrusion Detection & Prevention (IDS/IPS)
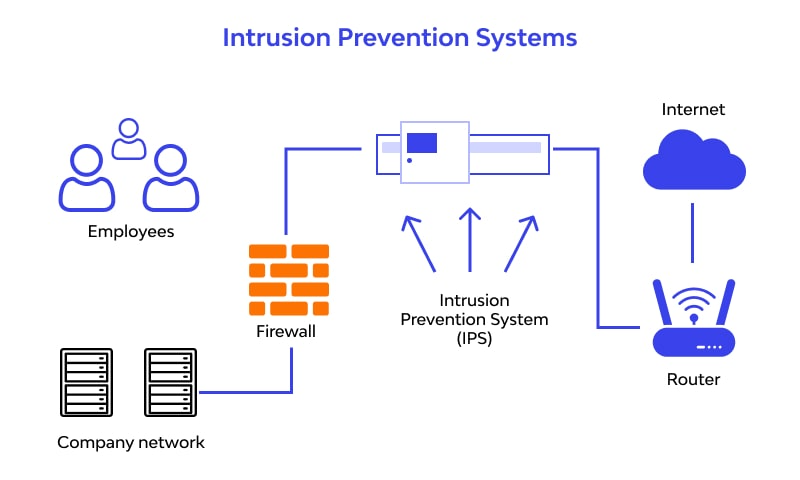
- Monitors network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Example Tools:
- Cisco Secure Firewall
- Darktrace (AI-based threat detection)
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Prevents sensitive data leaks.
- Example Tools:
- Symantec CloudSOC
- Microsoft Purview
6. Zero Trust Security Model
- “Never trust, always verify” approach.
- Example Tools:
- Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
- Okta (for identity verification)
Top Cloud Security Tools in 2024
| Tool | Provider | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Shield | Amazon | DDoS protection |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Microsoft | Threat detection & compliance |
| Google Cloud Security Command Center | Asset monitoring & threat detection | |
| Check Point CloudGuard | Check Point | Network security & posture management |
| Trend Micro Cloud One | Trend Micro | Workload & application security |
Future Trends in Cloud Security
- AI & Machine Learning for Threat Detection
- Quantum Encryption
- Serverless Security
Conclusion
Cloud security is not optional—it’s a necessity. With cyber threats evolving daily, businesses must adopt multi-layered security strategies using IAM, encryption, CSPM, and Zero Trust principles.
By leveraging advanced tools like AWS Shield, Prisma Cloud, and Microsoft Defender, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
Final Thoughts
- Regular security audits are crucial.
- Employee training reduces human error risks.
- Stay updated with the latest cloud security trends.
For more in-depth guides on cybersecurity and cloud computing, visit CupsDeeps.