Welcome to your complete beginner’s guide to cybersecurity — whether you’re a student, a small business owner, or just someone who wants to protect their personal data online, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know to get started in cybersecurity.
What Is Cybersecurity?
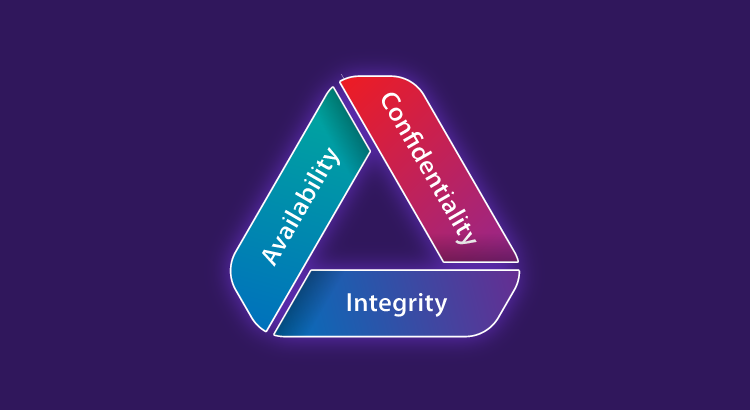
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting digital systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage. It involves a combination of technologies, processes, and practices designed to safeguard sensitive information and ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of digital assets.
“Cybersecurity is not just about technology—it’s about people, processes, and awareness.” – Cybersecurity Survival Guide
At its core, cybersecurity revolves around three fundamental principles:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of data.
- Availability: Guaranteeing that systems and data are accessible when needed.
Why Cybersecurity Matters Today
In today’s interconnected world, cyber threats are more sophisticated than ever. With the rise of remote work, cloud computing, and mobile devices, the digital landscape has expanded dramatically — and so have the opportunities for attackers.
Key Trends Driving Cybersecurity Needs:
- Cloud Adoption: More businesses are moving to cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP, increasing exposure to new risks.
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD): Employees using personal devices for work can introduce vulnerabilities.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart devices expand the attack surface.
- SaaS Applications: Tools like Microsoft 365 and Salesforce are widely used but often poorly monitored.
The goal of modern cybersecurity is not to prevent all breaches — which is nearly impossible — but to reduce risk and improve response time when incidents occur.
Common Cyber Threats You Should Know
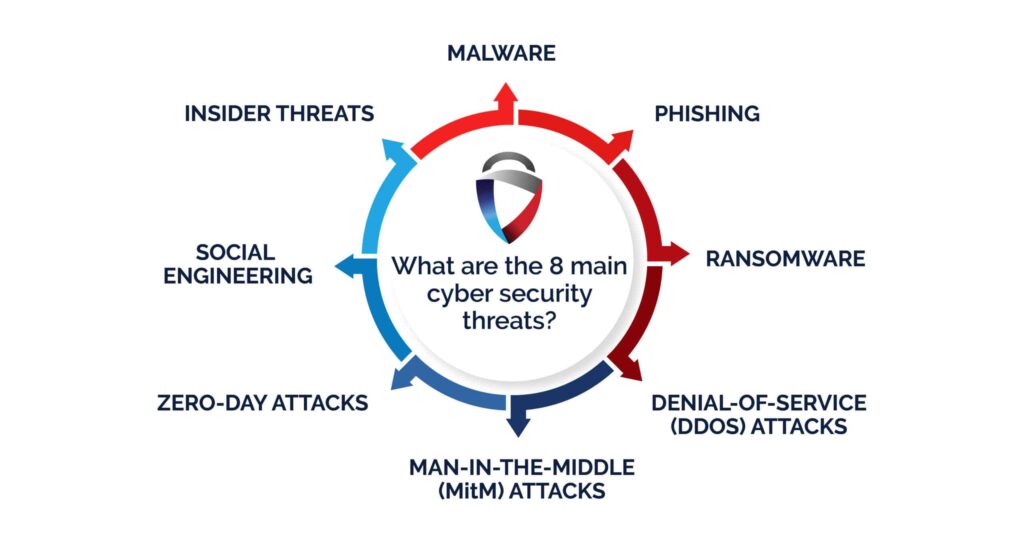
Understanding the types of threats you may face is essential for staying protected. Here are some of the most common cybersecurity threats:
| Threat Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Phishing | Fraudulent emails or websites designed to steal credentials or install malware. |
| Ransomware | Malicious software that encrypts files until a ransom is paid. |
| DDoS Attacks | Overwhelming a network with traffic to cause downtime. |
| Insider Threats | Employees or contractors misusing access rights. |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) | Intercepting communication between two parties. |
Other Emerging Threats:
- Watering Hole Attacks: Compromising frequently visited websites to infect visitors.
- Pharming: Redirecting legitimate website traffic to fake sites via DNS poisoning.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks that target unknown software vulnerabilities before patches are available.
💡 According to Symantec, watering hole attacks account for 24% of infection vectors used by targeted attack groups.
The Modern Cyber Attack Lifecycle
Cybercriminals rarely launch direct, brute-force attacks. Instead, they follow a structured path known as the Cyber-Attack Lifecycle:
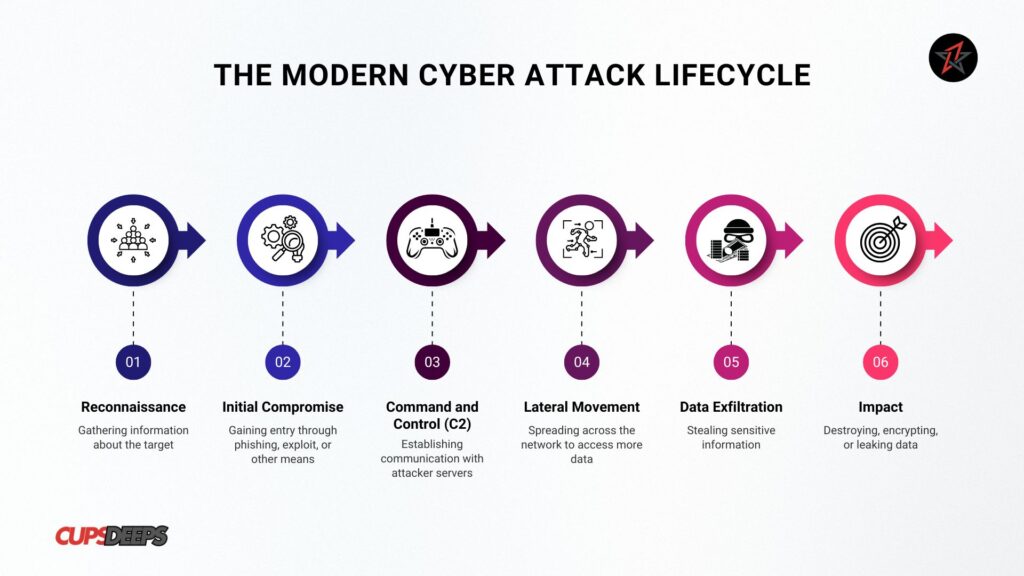
- Reconnaissance: Gathering information about the target.
- Initial Compromise: Gaining entry through phishing, exploit, or other means.
- Command and Control (C2): Establishing communication with attacker servers.
- Lateral Movement: Spreading across the network to access more data.
- Data Exfiltration: Stealing sensitive information.
- Impact: Destroying, encrypting, or leaking data.
This “low and slow” strategy allows attackers to remain undetected for long periods, sometimes even months.
Essential Cybersecurity Best Practices
Whether you’re an individual or part of an organization, adopting basic security habits can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
For Individuals:
- Use strong, unique passwords and a password manager.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible.
- Keep your software updated regularly.
- Be cautious with email attachments and suspicious links.
For Organizations:
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture — never trust, always verify.
- Deploy Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs).
- Conduct regular security audits and employee training.
- Monitor logs and use threat intelligence platforms.
🔒 Remember: Compliance does not equal security. Just because you meet regulatory requirements doesn’t mean you’re fully protected.
Understanding Cloud Security & Compliance
As more businesses move to the cloud, securing data becomes more complex. The shared responsibility model means cloud providers secure the infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their own data and applications.
Key Considerations:
- Visibility and Control: SaaS applications like Office 365 and Salesforce can be difficult to monitor without tools like Aperture™.
- Compliance Regulations:
- GDPR (Europe)
- HIPAA (Healthcare in the U.S.)
- SOX (Financial reporting compliance)
📊 Aperture provides deep analytics into user activity, helping organizations transition from speculation to knowing exactly what’s happening in their SaaS environments.
How to Get Started in Cybersecurity
If you’re new to cybersecurity and want to build a career or simply protect yourself better online, here’s how to begin:
Step-by-Step Roadmap:
- Learn Networking Basics: Understand TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP, and the OSI model.
- Study Operating Systems: Learn Windows, Linux, and macOS fundamentals.
- Master Cybersecurity Concepts: Study encryption, firewalls, and the CIA triad.
- Get Hands-On Experience: Try labs using tools like Wireshark, Kali Linux, and Metasploit.
- Explore Certifications: Start with CEH, CompTIA Security+, or Palo Alto Networks’ ACE.
📚 Palo Alto Networks offers free courses and certifications to help beginners enter the field.
Top Tools & Certifications for Beginners
🔧 Recommended Tools:
- Wireshark – Network protocol analyzer
- Nmap – Network discovery and security auditing
- Metasploit Framework – Penetration testing
- Splunk – Log analysis and SIEM
- AutoFocus / WildFire – Threat intelligence and malware analysis
🏆 Top Entry-Level Certifications:
| Certification | Provider | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| CompTIA Security+ | CompTIA | General cybersecurity knowledge |
| CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) | EC-Council | Penetration testing |
| ACE (Accredited Configuration Engineer) | Palo Alto Networks | NGFW basics |
| PCNSE (Palo Alto Certified Network Security Engineer) | Palo Alto Networks | Advanced firewall configuration |
Monitoring, Reporting & Logging
Security teams must maintain visibility across their entire network. Tools like Panorama and the Palo Alto Networks Logging Service allow centralized log management and analysis, making it easier to detect anomalies and respond quickly.
Features Include:
- Centralized logging from physical and virtual firewalls
- Real-time threat detection
- Custom report generation and scheduling
- Integration with SIEM solutions for advanced monitoring
📋 Reports can be filtered and scheduled for email delivery, ensuring stakeholders stay informed.
Threat Intelligence & Automation
Modern cybersecurity relies heavily on automation and intelligence sharing. Platforms like AutoFocus and MineMeld help organizations collect, filter, and analyze threat indicators from multiple sources.
Benefits:
- Correlates data from global threat feeds
- Identifies patterns in malicious behavior
- Enables proactive defense strategies
🔍 AutoFocus aggregates data from WildFire, PAN-DB, and Unit 42 research to provide actionable intelligence.
Endpoint Protection with Traps
Traps by Palo Alto Networks is an advanced endpoint protection platform designed to stop exploits and malware at the device level.
Key Capabilities:
- Blocks exploits targeting zero-day vulnerabilities
- Stops malware without relying on signatures
- Provides detailed forensics for incident investigation
- Integrates with NGFWs for coordinated threat prevention
Courses like Traps 4.2: Install, Configure, and Manage (EDU-281) and Traps 4.2: Deploy and Optimize (EDU-285) offer hands-on training for deploying Traps in enterprise environments.
ITIL & Help Desk Fundamentals
For those interested in enterprise-level operations, understanding ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is crucial. ITIL outlines best practices for IT service management, including:
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operation
- Continual Service Improvement
These frameworks help align cybersecurity practices with broader organizational goals.
Conclusion: Staying Secure in a Digital World
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process — not a one-time fix. As technologies evolve, so do threats. Whether you’re an individual user or part of a growing business, staying informed and proactive is the key to staying safe online.
“The goal isn’t to prevent all breaches — it’s to reduce risk and improve response time.” – Cybersecurity Survival Guide
Start small, stay consistent, and keep learning. With the right mindset and tools, anyone can build a strong foundation in cybersecurity.
🔗 Related Resources
📢 Call to Action (CTA)
Want more beginner-friendly guides on cybersecurity? Subscribe to our newsletter and get the latest updates, tips, and tutorials straight to your inbox!

